After several days of unusually high temperatures, the Conger ice shelf has collapsed in East Antarctica.

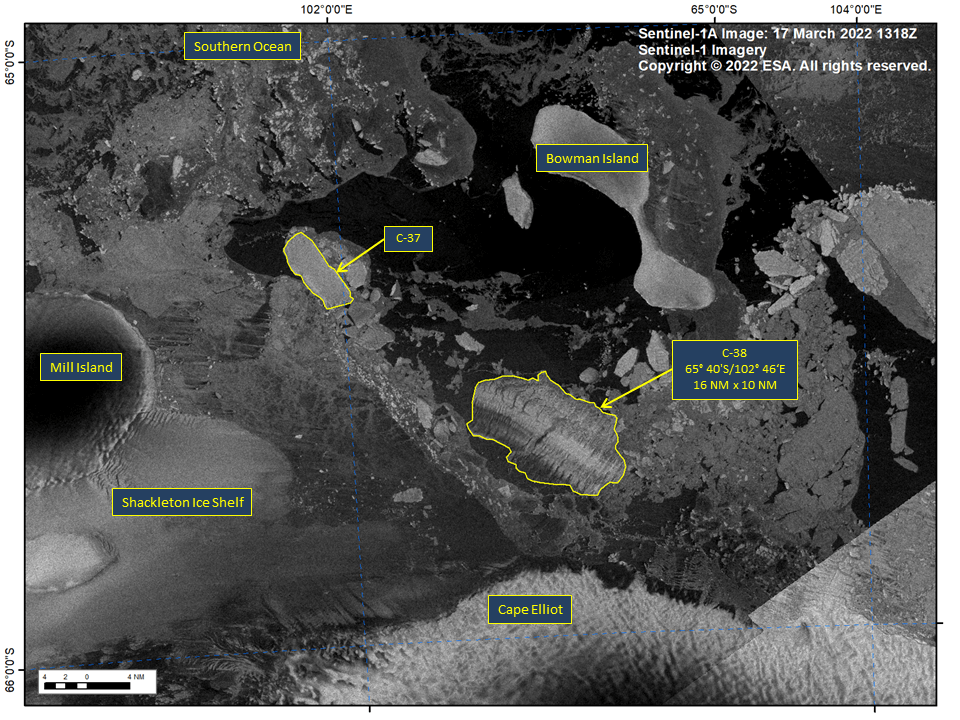
The U.S. National Ice Center reported the break on March 17, sharing satellite images of the Conger ice shelf, which had broken free of the Wilkes Land Region before losing Iceberg C-38, which made up “virtually all that remained of the Conger ice shelf.”
The Conger ice shelf had a surface area of 16 nautical miles (approximately 30 kilometres) in length and 10 nautical miles (approximately 18 kilometres) in width before Iceberg C-38 calved. Calving occurs when ice chunks break from the edge of a glacier, iceberg or ice shelf and crash into the water.
There have been unusually high temperatures in Antarctica recently, with Concordia Station publishing record temperatures of -11.8 degrees Celsius on March 18, 40 degrees warmer than normal for the season. The warming is likely a result of a random weather event and not a sign of climate change.
Ice shelves, according to the National Snow and Ice Data Center, are permanent floating ice sheets that connect to a landmass. Without these masses, inland ice moves faster into ocean waters, raising sea levels.
Dr Catherine Colello Walker, an earth and planetary scientist at Nasa and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, told The Guardian the loss of the Conger ice shelf “is one of the most significant collapse events anywhere in Antarctica since the early 2000s.”
“It won’t have huge effects, most likely, but it’s a sign of what might be coming,” Walker said.
In February, the Antarctic sea ice annual maximum extent — or the total area covered by some amount of ice, including open water between ice floes — reached a low.
Sea ice extent was measured at 14.88 million square kilometres, the 10th-lowest mass in existing satellite records.
- Iranian warship sunk by the U.S. was returning from an exhibition
- U.S. House to vote on halting Iran war after Senate defeats similar measure
- ‘An eyesore’: Trump’s White House ballroom plans receive deluge of public comments
- Iran pummelled by new airstrikes as it launches attacks on Israel, U.S. bases










Comments
Want to discuss? Please read our Commenting Policy first.