WATCH: Some scientists have spent their entire careers working on the Rosetta space probe, which made its way to the surface of a speeding comet on Wednesday. Teams from around the world, including from Canada, have helped get this project off the ground. Reid Fiest reports.

TORONTO – The European Space Agency’s Philae probe became the first to land on a comet on Wednesday. If you don’t think that’s pretty cool, here are some reasons that may change your mind.
1. The comet was moving at 60,000 km/h
The landing has been described as trying to catch a bullet with another bullet — clearly, no easy task.
Think about a merry-go-round. Have you ever tried to grab someone’s hand or jump on as it spins? It’s kind of like that (but straight).
2. It will give us some insight into how life may have started on Earth
One of the biggest questions that has plagued scientists is: How did life on Earth begin?
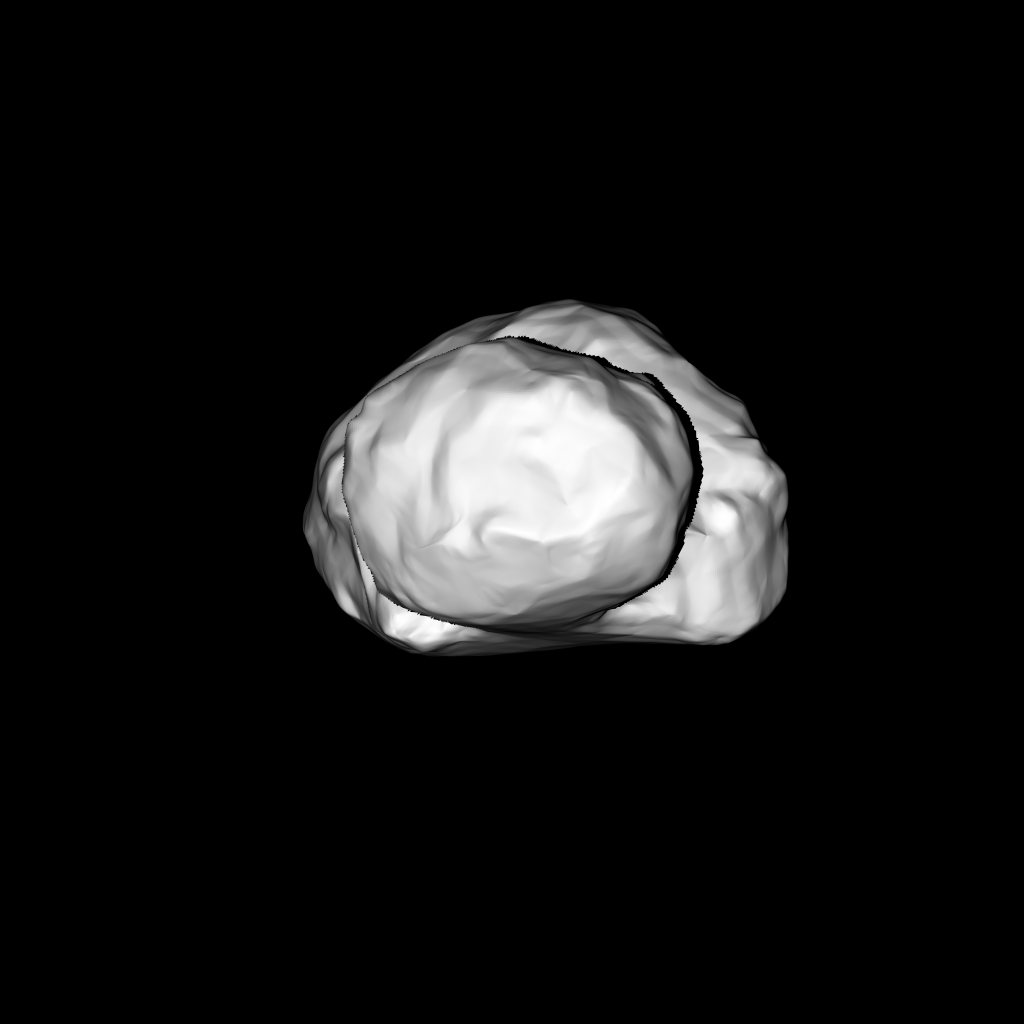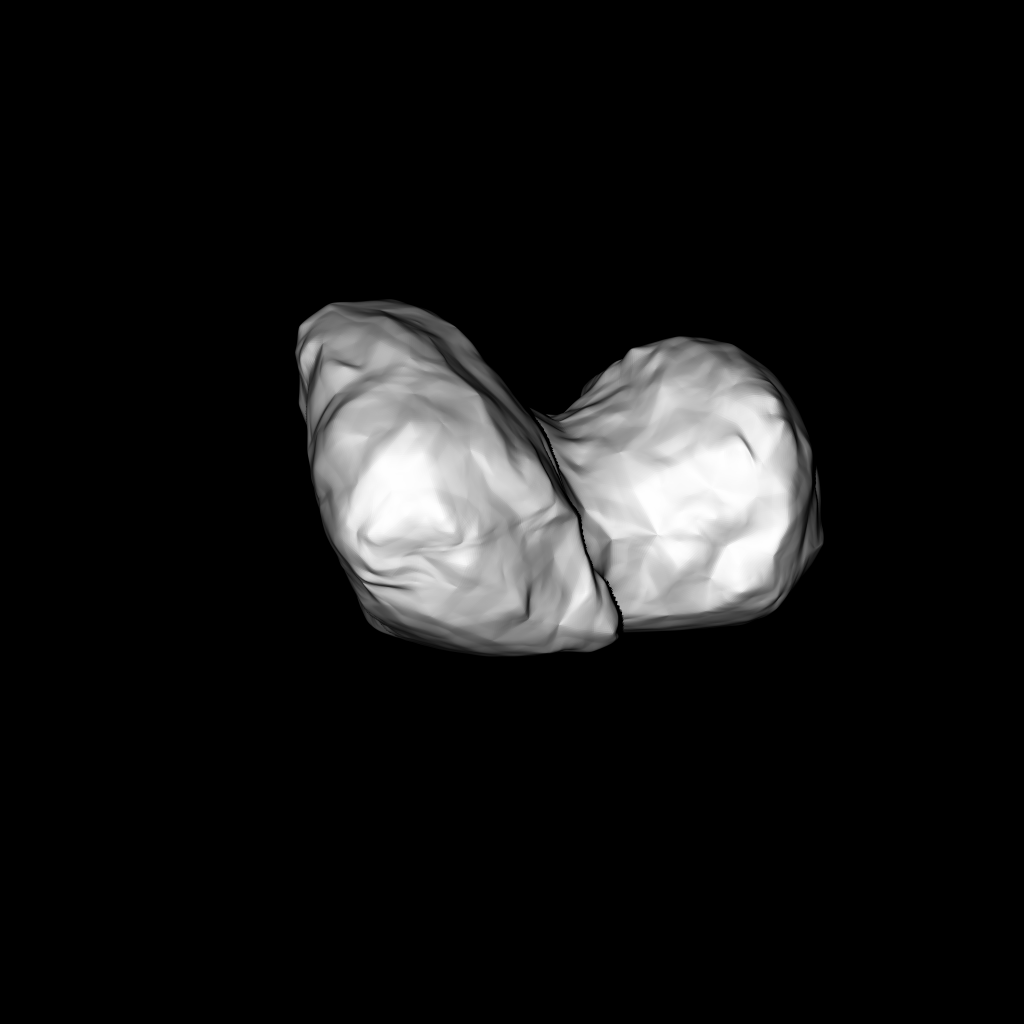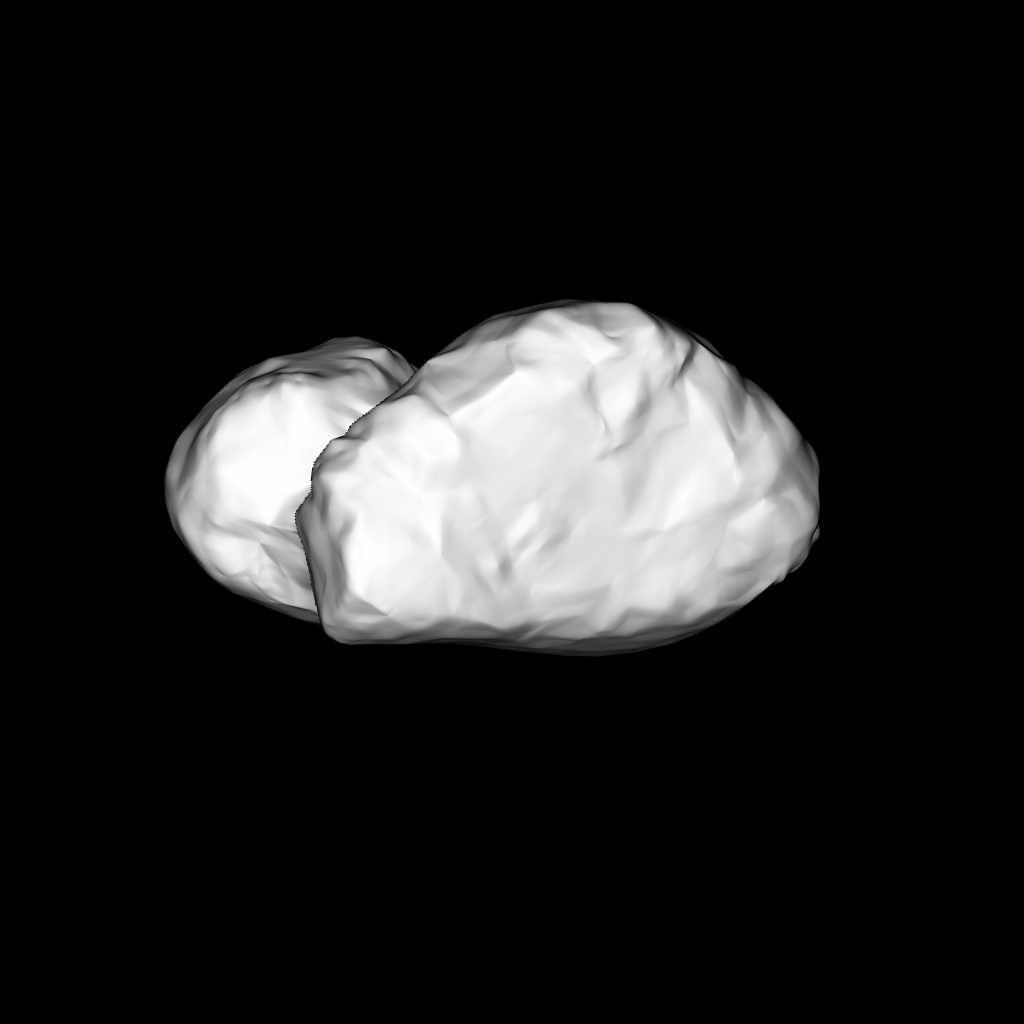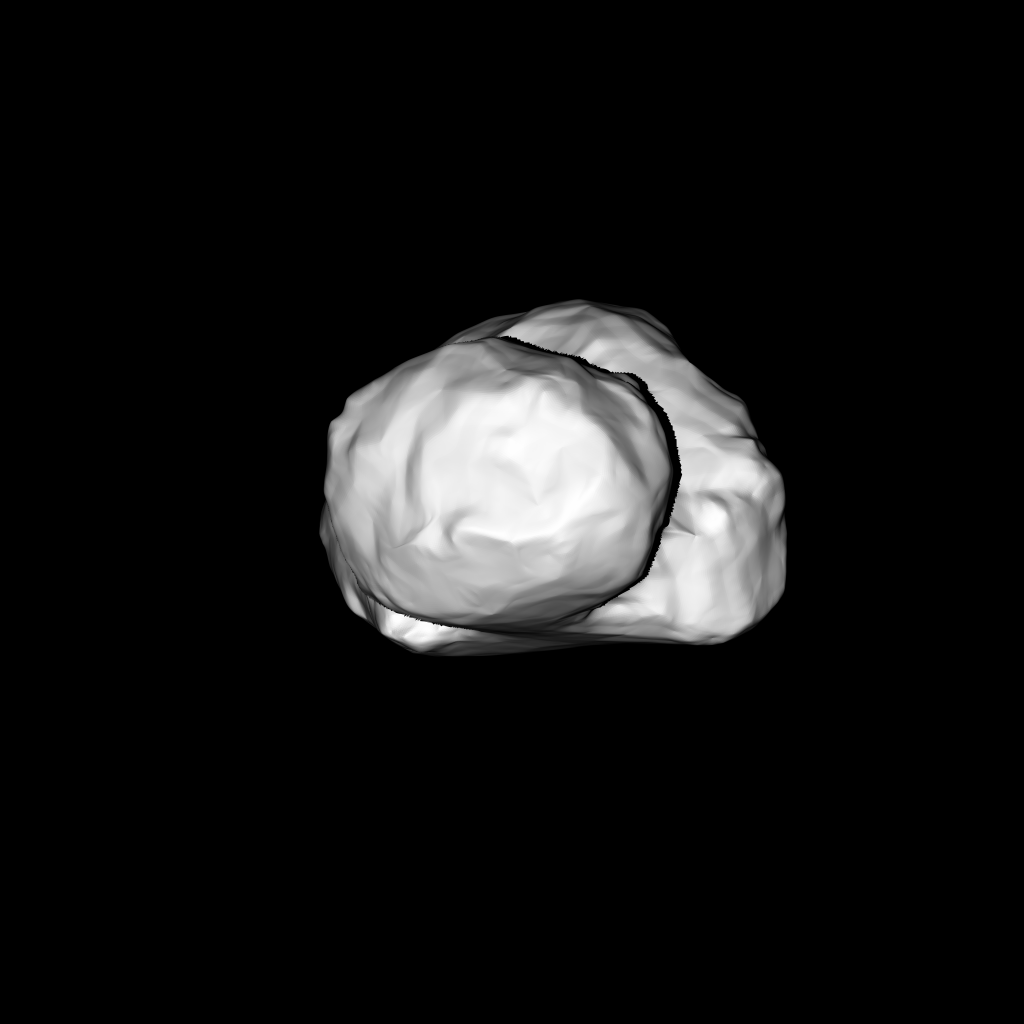
Comets are some of the oldest bodies in our solar system, which formed 4.5 billion years ago. Not only that, but comets contain complex organic compounds that are essential to life as we know it, such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen.
Rosetta’s mission — and the Philae lander — aims to provide astronomers and scientists with information as to the composition of comets.
3. Philae is on for the long haul

Get daily National news
Philae’s ultimate goal is to further understand the changing properties of comets as they encounter ever-increasing solar radiation.
Comets are often referred to as “dirty snowballs.” They are comprised of dust and ice and, as they move along, radiation from the sun sublimates the particles. This creates the tail that we associate with comets.
The current mission ends on Dec. 31, 2015 — after the comet gets to its closest point around the sun. But that’s not the end of Rosetta. The mission’s planned lifetime is 12 years as it follows Comet 67/P Churyumov-Geramisenko back out to the outer solar system.
4. It took 10 years and travelled 6.4 billion kilometres
While Comet 67/P Churyumov-Gerasimenko is about 500 million km away, the Rosetta spacecraft took a long and circuitous route to get there.
Rosetta utilized gravity-assist maneouvres to get to the comet. Gravity assists swing spacecraft around planets and slingshot them around, giving the spacecraft a significant increase in speed. Rosetta did four planetary gravity assists: three of Earth, in 2005, 2007 and 2009, and one of Mars, in 2007.
5. It landed on a comet!
That Rosetta’s Philae probe made it to the surface of a comet has to be one of the coolest things about this mission.
It has never been done. History was made today. The future is now.






Comments
Want to discuss? Please read our Commenting Policy first.