TORONTO – Imagine looking up at the night sky and seeing a star that you’d never noticed before. That’s just what happened to Japanese astronomer Koichi Itagaki.

On Aug. 14, amateur astronomer Itagaki discovered a bright “new” star in the constellation of Delphinus while using a 0.18-metre telescope with a charged-coupling device (CCD) camera. These cameras are highly sensitive and are used by professional and amateur astronomers to photograph the night sky.
Though the star had actually been there before, it had been significantly dimmer. In fact, some astronomers believe that the star has brightened by almost 25,000 times. The star is located within our galaxy.
Animation of nova by E. Guido & N. Howes
Why has the star brightened?
The star’s brightening was caused by a nova.
Novas (or novae) occur as part of a binary (two-star) system. It is believed that a normal star, much like our sun, and a small, dense star — called a white dwarf — orbit closely to one another. The white dwarf pulls in hydrogen gas from the other star and, because the white dwarf is so dense, it compresses the gas.
If enough of the hydrogen builds up on the surface, it can fuse into helium which releases a large amount of energy, thus causing the star to brighten over time and then fade once again.
“The process can be repeated over and over again over periods of hundreds to thousands of years,” said Randy Attwood, an astronomer and president of Earthshine, an astronomy education organization based out of Mississauga, Ont.
Novas are not related to supernovas, which are exploding stars that can sometimes outshine the galaxy they’re in.
The word “nova” comes from Latin which means “new.” Ancient astronomers used this name when previously unseen stars would appear in the sky. Supernova were thought to be just super bright novas.
Astronomers are excited about the discovery because it allows them to further study and understand the process of a nova.
Astronomers don’t know how far away the star is, however, it likely went through this process billions of years ago. That means we are looking back in time — the star may not even be there anymore.
“Scientifically this is something astronomers will continue to observe and study,” Attwood said. “Amateurs can go out and make estimates of the brightness of the star, watching it slowly wane over time until in weeks or months it will be only visible through large telescopes.”
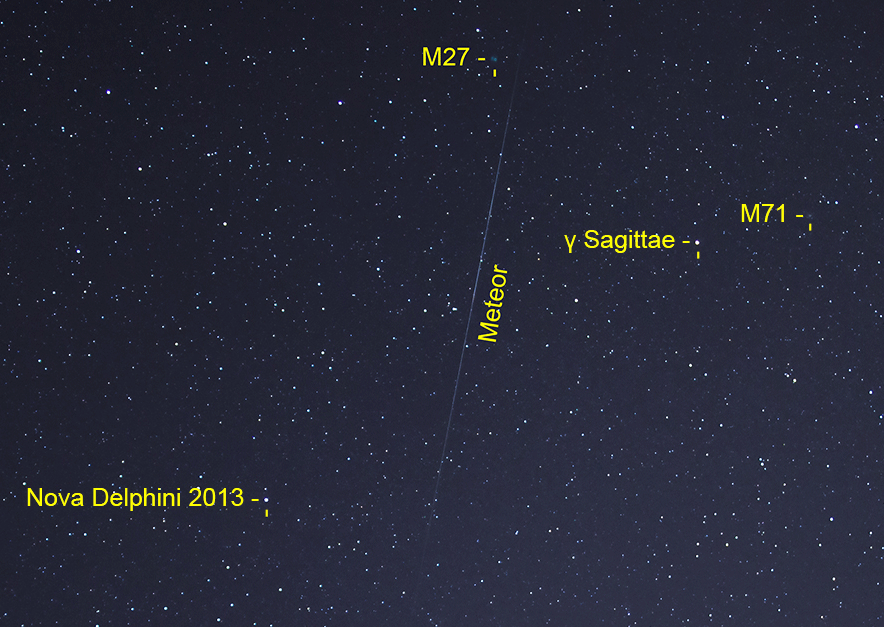
Where to find the nova
Though the full moon might make it difficult to spot the nova with the naked eye, over the next few days, you can always use binoculars or a telescope.
A nova this bright isn’t very common.
“A nova which you can see without optical aid is quite rare,” Attwood said. “There was a rather bright one in August 1975 which was brighter than the stars in the Big Dipper.”
Since the discovery, the star has continued to brighten, though it is believed that it has reached its maximum brightness.
So tonight, if you have a clear sky, go outside, look up, and watch the universe live and breathe.



Comments